Health impacts: particles and coal dust: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (14 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Airborne Particles == | == Airborne Particles == | ||
Exposure to air pollution––especially particles––is the second leading risk factor for mortality globally (behind only high blood pressure), contributing to approximately 8 million deaths each year.<ref>State of Global Air, [https://www.stateofglobalair.org/hap#:~:text=Air%20pollution%20accounts%20for%20more,1%20year%20and%208%20months. Health Impacts of Air Pollution].</ref> Particles are very harmful,<ref>American Lung Association, State of the Air, | Exposure to air pollution––especially particles––is the second leading risk factor for mortality globally (behind only high blood pressure), contributing to approximately 8 million deaths each year.<ref>State of Global Air, [https://www.stateofglobalair.org/hap#:~:text=Air%20pollution%20accounts%20for%20more,1%20year%20and%208%20months. Health Impacts of Air Pollution].</ref> Particles are very harmful,<ref>American Lung Association, [[:File:State-of-the-Air-2025.pdf|State of the Air]], Health Impact of Air Pollution, 2025.</ref><ref>U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, [[:File:ISA PM FINAL2019.PDF|Integrated Science Assessment (ISA) for Particulate Matter]], 2019.</ref><ref>Liu et al., [https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa1817364 Ambient Particulate Air Pollution and Daily Mortality in 652 Cities], ''The New England Journal of Medicine'', 381, 8, 705–715, 2019.</ref> with chronic exposure to particulates shortening our lives by an average of 1–3 years.<ref>State of Global Air, [https://www.stateofglobalair.org/health/life-expectancy Impact of Air Pollution on Life Expectancy].</ref><ref>Greenstone et al., Air Quality Life Index, Annual Update, 2024.</ref><ref>Pope III et al., [https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMsa0805646 Fine-Particulate Air Pollution and Life Expectancy in the United States], ''The New England Journal of Medicine'', 360, 4, 376–386, 2009.</ref> Chronic and acute exposure to particles has also been linked to: increased risk of death from cardiovascular disease;<ref>Dockery et al., [https://www.nejm.org/doi/10.1056/NEJM199312093292401 An Association between Air Pollution and Mortality in Six U.S. Cities], ''The New England Journal of Medicine'', 329, 24, 1753–1759, 1993.</ref><ref>Pope et al., [https://www.atsjournals.org/doi/abs/10.1164/ajrccm/151.3_Pt_1.669?role=tab Particulate Air Pollution as a Predictor of Mortality in a Prospective Study of U.S. Adults], ''American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine'', 151, 3, 1995.</ref><ref>Brunekreef et al., [https://www.n65.nl/NCLS-AIR-Study-2009.pdf Effects of Long-Term Exposure to Traffic-Related Air Pollution on Respiratory and Cardiovascular Mortality in the Netherlands: The NLCS-AIR Study], Health Effect Institute Research Report, 139, 2009.</ref><ref>Eftim et al., [https://journals.lww.com/epidem/fulltext/2008/03000/fine_particulate_matter_and_mortality__a.9.aspx Fine Particulate Matter and Mortality: A Comparison of the Six Cities and American Cancer Society Cohorts with a Medicare Cohort], ''Epidemiology'', 19, 2, 209–216, 2008.</ref><ref>Laden et al., [https://www.atsjournals.org/doi/10.1164/rccm.200503-443OC Reduction in Fine Particulate Air Pollution and Mortality: Extended Follow-Up of the Harvard Six Cities Study], ''American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine'', 173, 6, 667–672, 2006.</ref><ref>Miller et al., [https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa054409 Long-Term Exposure to Air Pollution and Incidence of Cardiovascular Events in Women], ''The New England Journal of Medicine'', 356, 5, 447–458, 2007.</ref><ref>Pope III et al., [https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/01.CIR.0000108927.80044.7F Cardiovascular Mortality and Long-Term Exposure to Particulate Air Pollution: Epidemiological Evidence of General Pathophysiological Pathways of Disease], ''Circulation'', 109, 1, 71–77, 2004.</ref><ref>Puett et al., [https://academic.oup.com/aje/article/168/10/1161/2739694 Chronic Particulate Exposure, Mortality, and Coronary Heart Disease in the Nurses’ Health Study], ''American Journal of Epidemiology'', 168, 10, 1161–1168, 2008.</ref><ref>Puett et al., [https://ehp.niehs.nih.gov/doi/10.1289/ehp.0900572 Chronic Fine and Coarse Particulate Exposure, Mortality, and Coronary Heart Disease in the Nurses’ Health Study], ''Environmental Health Perspectives'', 117, 11, 1697–1701, 2009.</ref><ref>Samet et al., [https://www.nejm.org/doi/10.1056/NEJM200012143432401 Fine Particulate Air Pollution and Mortality in 20 U.S. Cities, 1987–1994], ''The New England Journal of Medicine'', 343, 24, 1742–1749, 2000.</ref><ref>Zanobetti et al., [https://ehp.niehs.nih.gov/doi/full/10.1289/ehp.0800108 The Effect of Fine and Coarse Particulate Air Pollution on Mortality: A National Analysis], ''Environmental Health Perspectives'', 117, 6, 898–903, 2009.</ref> diminished lung function and damage to the small airways of the lungs;<ref>Wu et al., [https://ehp.niehs.nih.gov/doi/10.1289/ehp.0901159 Case Report: Lung Disease in World Trade Center Responders Exposed to Dust and Smoke: Carbon Nanotubes Found in the Lungs of World Trade Center Patients and Dust Samples], ''Environmental Health Perspectives'', 118, 4, 499–504, 2010.</ref><ref>Zhang et al., [https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/indhealth/55/1/55_2016-0031/_article Long-Term Exposure to Diesel Engine Exhaust Induced Lung Function Decline in a Cross Sectional Study], ''Industrial Health'', 55, 1, 13–26, 2017.</ref><ref>Cui et al., [https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapediatrics/fullarticle/2763826 Association between Bedroom Particulate Matter Filtration and Changes in Airway Pathophysiology in Children with Asthma], ''Journal of the American Medical Association Pediatrics'', 174, 6, 533–542, 2020.</ref><ref>Karr et al., [https://academic.oup.com/aje/article/165/5/553/67083?login=true Effects of Subchronic and Chronic Exposure to Ambient Air Pollutants on Infant Bronchiolitis], ''American Journal of Epidemiology'', 165, 5, 553–560, 2007.</ref><ref>Leikauf et al., [https://www.nature.com/articles/s12276-020-0394-0 Mechanisms of Ultrafine Particle-Induced Respiratory Health Effects], ''Experimental & Molecular Medicine'', 52, 329–337, 2020. </ref> increased hospitalization for asthma attacks for children;<ref>Altman et al., [https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2542519622003023?via%3Dihub Relationships of Outdoor Air Pollutants to Non-Viral Asthma Exacerbations and Airway Inflammatory Responses in Urban Children and Adolescents: A Population-Based Study], ''The Lancet Planetary Health'', 7, 1, e33–e44, 2023.</ref><ref name=":0" /><ref>Tolbert et al., [https://academic.oup.com/aje/article/151/8/798/116838?login=true Air Quality and Pediatric Emergency Room Visits for Asthma in Atlanta, Georgia, USA], ''American Journal of Epidemiology'', 151, 798–810, 2000.</ref><ref>Schwartz et al., [https://www.atsjournals.org/doi/abs/10.1164/ajrccm/147.4.826 Particulate Air Pollution and Hospital Emergency Room Visits for Asthma in Seattle], ''American Review of Respiratory Disease'', 147, 826–31, 1993.</ref> slowed lung function growth in children and teenagers;<ref>Garcia et al., [https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0091674921008083?via%3Dihub Air Pollution and Lung Function in Children], ''Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology'', 148, 1, 1–14, 2021.</ref><ref>Raizenne et al., [https://ehp.niehs.nih.gov/doi/10.1289/ehp.8979179 Acute lung Function Responses to Ambient Acid Aerosol Exposures in Children], ''Environmental Health Perspectives'', 79, 179–85, 1989.</ref><ref>Thurston et al., [https://www.atsjournals.org/doi/10.1164/ajrccm.155.2.9032209 Summertime Haze Air Pollution and Children with Asthma], ''American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine'', 155, 654–660, 1997.</ref> increased risk of lower birth weights and infant mortality;<ref>Fong et al., [https://journals.lww.com/epidem/fulltext/2019/09000/fine_particulate_air_pollution_and_birthweight_.2.aspx Fine Particulate Air Pollution and Birthweight: Differences in Associations along the Birthweight Distribution], ''Epidemiology'', 30, 5, 617–623, 2020.</ref><ref>Basu et al., [https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0013935113001837?via%3Dihub Effects of Fine Particulate Matter and Its Constituents on Low Birth Weight among Full-Term Infants in California], ''Environmental Research'', 128, 42–51, 2014.</ref><ref>Dadvand et al., [https://ehp.niehs.nih.gov/doi/10.1289/ehp.1205575 Maternal Exposure to Particulate Air Pollution and Term Birth Weight: A Multi-Country Evaluation of Effect and Heterogeneity], ''Environmental Health Perspectives'', 121, 3, 267–373, 2013.</ref><ref>Ebisu et al., [https://ehp.niehs.nih.gov/doi/10.1289/ehp.1104763 Airborne PM<sub>2.5</sub> Chemical Components and Low Birth Weight in the Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic Regions of the United States], ''Environmental Health Perspectives'', 120, 12, 1746–1752, 2012.</ref><ref>Kloog et al., [https://ehjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1476-069X-11-40 Using New Satellite Based Exposure Methods to Study the Association between Pregnancy PM<sub>2.5</sub> Exposure, Premature Birth and Birth Weight in Massachusetts], ''Environmental Health'', 11, 40, 2012.</ref><ref>Stieb et al., [https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0013935112001764?via%3Dihub Ambient Air Pollution, Birth Weight and Preterm Birth: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis], ''Environmental Research'', 117, 100–111, 2012. </ref> elevated risk of developing type-2 diabetes;<ref>Eze et al., [https://ehp.niehs.nih.gov/doi/10.1289/ehp.1307823 Association between Ambient Air Pollution and Diabetes Mellitus in Europe and North America: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis], ''Environmental Health Perspectives'', 123, 5, 381-389, 2015.</ref><ref>Liu et al., [https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S026974911930257X?via%3Dihub Associations between Long-Term Exposure to Ambient Air Pollution and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis], ''Environ Pollution'', 252, ptB, 1235–1245, 2019.</ref><ref>Wu et al., [https://bmcmedicine.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12916-022-02573-0 Ambient Air Pollution Associated with Incidence and Dynamic Progression of Type 2 Diabetes: A Trajectory Analysis of a Population‑Based Cohort], ''BMC Medicine'', 20, 375, 2022.</ref> cognitive impacts, including links to dementia, Alzheimer’s Disease, and Parkinson’s Disease;<ref>Weuve, et al., [https://ehp.niehs.nih.gov/doi/10.1289/EHP8716 Exposure to Air Pollution in Relation to Risk of Dementia and Related Outcomes: An Updated Systematic Review of the Epidemiological Literature], ''Environmental Health Perspectives,'' 129, 96001, 2021.</ref><ref>Shi et al., [https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanplh/article/PIIS2542-5196(20)30227-8/fulltext Long-Term Effects of PM<sub>2.5</sub> on Neurological Disorders in the American Medicare Population: A Longitudinal Cohort Study], ''Lancet Planetary Health'', 4, e557–e565, 2020.</ref><ref>Shi et al., [https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2211282119 Incident Dementia and Long-Term Exposure to Constituents of Fine Particle Air Pollution: A National Cohort Study in the United States], ''Proceeding of the National Academy of Sciences U.S.A.'', 120, e2211282119, 2022.</ref><ref>Peters, [https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2220028120 Commentary: Ambient Air Pollution and Alzheimer’s Disease: The Role of the Composition of Fine Particles], ''Proceeding of the National Academy of Sciences U.S.A.'', 120, 3, e2220028120, 2023.</ref> and increased risk of mental health issues such as depression.<ref>Gao X et al., Long-Term Air Pollution, [https://ehp.niehs.nih.gov/doi/10.1289/EHP10391 Genetic Susceptibility, and the Risk of Depression and Anxiety: A Prospective Study in the UK Biobank Cohort], ''Environmental Health Perspectives'', 131, 1, 2023.</ref> There is no safe level of exposure to particle pollution.<ref name=":10">Wei et al., [https://www.bmj.com/content/384/bmj-2023-076939 Exposure-Response Associations between Chronic Exposure to Fine Particulate Matter and Risks of Hospital Admission for Major Cardiovascular Diseases: Population Based Cohort Study], ''BMJ'', 384, e076939, 2024.</ref><ref name=":11">Sun et al., [https://www.bmj.com/content/384/bmj-2023-076322 Short Term Exposure to Low Level Ambient Fine Particulate Matter and Natural Cause, Cardiovascular, and Respiratory Morbidity among US Adults with Health Insurance: Case Time Series Study], ''BMJ'', 384, e076322, 2024.</ref> | ||
The health impacts of particles are influenced by particle size, composition, and shape. | The health impacts of particles are influenced by particle size, composition, and shape. | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
== Coal Dust == | == Coal Dust == | ||
The majority of research on the health impacts of coal dust | [[File:Example CWP.jpg|alt=Photograph of a lung that healthy (left), with simple black lung disease (center), and complicated black lung disease (right).|thumb|Photograph of a lung that is healthy (left), with moderate black lung disease (center), and severe black lung disease (right).<ref>Popovich, [https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2018/02/22/climate/black-lung-resurgence.html Black Lung Disease Comes Storming Back in Coal Country], ''New York Times'', February 22, 2018.</ref>]] | ||
Coal dust is a component of particulate matter. The majority of research on the health impacts of coal dust has come from studies on occupational exposures of coal miners. Miners’ inhalation exposure to coal dust has been shown to place them at an increased risk of developing Coal Workers’ pneumoconiosis (CWP), also known as coal miner’s lung, black lung disease, or progressive massive fibrosis, as well as lung cancer, decreased lung function, and other health impacts.<ref name=":12">Liu et al., [https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0013935120307441 The Impacts of Coal Dust on Miners’ Health: A Review], ''Environmental Research'', 190, 109849, 2020.</ref><ref>Attfield et al., Occupational and Environmental Respiratory Disease, St. Louis, MO, Mosby, 362–372, 1996.</ref><ref>American Lung Association, [https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/black-lung/learn-about-black-lung Learn About Coal Worker’s Pneumoconiosis], 2024.</ref><ref>Blackley et al., [https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2671456 Progressive Massive Fibrosis in Coal Miners From 3 Clinics in Virginia], ''Journal of the American Medical Association'', 319, 5, 500-501, 2018.</ref><ref>United States Government Accountability Office, [[:File:Gao-12-832r.pdf|MINE SAFETY: Reports and Key Studies Support the Scientific Conclusions Underlying the Proposed Exposure Limit for Respirable Coal Mine Dust]], August 17, 2012.</ref> | |||
Coal dust typically contains high levels of toxic metals, including mercury (Hg), lead (Pb), arsenic (Ar), cadmium (Cd), as well as crystalline silica. | Coal dust typically contains high levels of toxic metals, including mercury (Hg), lead (Pb), arsenic (Ar), cadmium (Cd), as well as crystalline silica. These substances are harmful when inhaled or ingested and are known to cause cancer, fetal defects, and neurological damage, even at very low doses. Coal dust also contains high levels of transition metals, including iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), and copper (Cu) that can induce oxidative stress in our bodies.<ref name=":12" /> Because coal dust has high concentrations of metals, there is reason to believe it causes harm at exposures below [[Particulate matter and coal dust|PM<sub>10</sub>]] [[Regulation under the Clean Air Act|National Ambient Air Quality Standards]], with there being so safe level of [[Particulate matter and coal dust|PM<sub>2.5</sub>]] composed of any material.<ref name=":10" /><ref name=":11" /> Researchers have measured elevated metals with known health impacts in the soils near coals mines and terminals, for example, selenium (Se) in the vicinity of mountaintop coal mines in the Elk Valley, British Columbia, Canada<ref>Petryshen et al., [https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S240584402304450X Spatial Distribution of Selenium and other Potentially Toxic Elements Surrounding Mountaintop Coal Mines in the Elk Valley, British Columbia, Canada], ''Heliyon'', 9, 7, e17242, 2023.</ref> and arsenic near the Norfolk Southern Terminal in Lambert's Point, Norfolk.<ref>Bounds et al., [https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11270-007-9442-9 Arsenic Addition to Soils from Airborne Coal Dust Originating at a Major Coal Shipping Terminal], ''Water, Air, and Soil Pollution'' 185, 195–207, 2007.</ref> | ||
There is a body of research identifying an array of adverse health impacts on communities living near coal mines and areas of coal-related activities, particularly in Appalachia. These include: higher rates of lung, kidney, and heart disease, even for people who never worked in a mine; | There is a body of research identifying an array of adverse health impacts on communities living near coal mines and areas of coal-related activities, particularly in Appalachia<ref name=":3">Hendryx et al., [https://ajph.aphapublications.org/doi/full/10.2105/AJPH.2007.113472 Relations between Health Indicators and Residential Proximity to Coal Mining in West Virginia], ''American Journal of Public Health'', 98, 4, 669–671, 2008.</ref><ref name=":4">Zulling et al., [https://ajph.aphapublications.org/doi/full/10.2105/AJPH.2010.300073 Health-Related Quality of Life Among Central Appalachian Residents in Mountaintop Mining Counties], ''American Journal of Public Health'', 101, 5, 848–853, 2011.</ref><ref name=":5">Hendryx, Mortality from Heart, [https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00420-008-0328-y Respiratory, and Kidney Disease in Coal Mining Areas of Appalachia], ''International Archives of Occupational and Environmental Health'', 82, 243–249, 2008.</ref><ref name=":6">Hendryx et al., [https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169500208000603 Lung Cancer Mortality is Elevated in Coal-Mining Areas of Appalachia], ''Lung Cancer'', 62, 1, 1–7, 2007.</ref><ref name=":7" /><ref name=":8">Hendryx et al., [https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0091743509004319 Higher Coronary Heart Disease and Heart Attack Morbidity in Appalachian Coal Mining Regions], ''Preventive Medicine'', 49, 5, 355–359, 2009. </ref><ref name=":9">Hendryx et al., [https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/15287390701601236?journalCode=uteh20 Hospitalization Patterns Associated with Appalachian Coal Mining], ''Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health'', 24, 2064–2070, 2007. </ref> but other locations as well.<ref name=":2">Brabin et al., [https://adc.bmj.com/content/70/4/305 Respiratory Morbidity in Merseyside Schoolchildren Exposed to Coal Dust and Air Pollution], ''Archives of Disease in Childhood'', 70, 4, 305–312, 1994.</ref><ref name=":13">Yapici et al., [https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/0748233706071740 Lead and Cadmium Exposure in Children Living around a Coal-Mining Area in Yatağan, Turkey], ''Toxicology and Industrial Health'', 22, 357–362, 2006.</ref><ref name=":14">Howel et al., [https://ehp.niehs.nih.gov/doi/10.1289/ehp.01109567 Consultations of Children Living near Open-Cast Coal Mines], ''Environmental Health Perspectives'', 109, 567–71, 2001.</ref><ref name=":15">Pless-Mulloli et al., [https://oem.bmj.com/content/57/3/145 Living near Opencast Coal Mining Sites and Children's Respiratory Health], ''Occupational & Environmental Medicine'', 57,145–51, 2000.</ref><ref name=":16">Santos et al., [https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0045653518300900?via%3Dihub Biomonitoring of Trace Elements in Urine Samples of Children from a Coal-Mining Region], ''Chemosphere'', 197, 622–626, 2018.</ref> These include: higher rates of lung, kidney, and heart disease, even for people who never worked in a mine; worse adjusted health status and with higher rates of cardiopulmonary disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and hypertension;<ref name=":3" /><ref name=":5" /><ref name=":8" /><ref name=":9" /> more days of self-rated poor physical and/or mental health and activity limitation;<ref name=":4" /><ref>Zullig et al., [https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/003335491012500410 A Comparative Analysis of Health-Related Quality of Life for Residents of U.S. Counties with and without Coal Mining], ''Public Health Reports'', 125, 548–555, 2010. </ref> higher mortality, including from lung cancer;<ref name=":6" /> more frequent birth defects;<ref name=":7">Ahern et al., [https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0013935111001484 The Association between Mountaintop Mining and Birth Defects among Live Births in Central Appalachia], 1996–2003. ''Environmental Research'', 111, 6, 838–846, 2011.</ref> more prevalent respiratory symptoms and/or more severe respiratory symptoms in elementary school-aged children that were exposed to coal dust;<ref name=":2" /><ref name=":14" /><ref name=":15" /> poorer learning outcomes;<ref>Cain et al., [https://www.liebertpub.com/doi/10.1089/env.2010.0001 Learning Outcomes among Students in Relation to West Virginia Coal Mining: an Environmental Riskscape Approach], ''Environmental Justice'', 3, 2, 71–77, 2010.</ref> and elevated lead and cadmium in the blood of children ages 6 months–6 years<ref name=":13" /> and elevated selenium and zinc in the urine of children ages 6–11 years<ref name=":16" /> living in coal-mining areas. | ||
Comparable studies have not been done to assess health impacts on residents living near coal export facilities in Hampton Roads. There are references to a 2005 study by the Peninsula Health District purporting to show that Southeast Newport News residents visited the emergency room for asthma at a rate double that of both Newport News and Virginia on average. | Comparable studies have not been done to assess health impacts on residents living near coal export facilities in Hampton Roads. There are references to a 2005 study by the Peninsula Health District purporting to show that Southeast Newport News residents visited the emergency room for asthma at a rate double that of both Newport News and Virginia on average. However, a copy of the document can not be found. | ||
[[Interviews and Oral Histories|Interviews with residents]] of Southeast Newport News and Lambert’s Point reveal that asthma and other respiratory health impacts are widespread and a major issue of community concern. One resident of Southeast Newport News, Uneita Scott, reported that her sister became sick from exposure to coal dust as a child: "Her diagnosis was a coal miner's lung so they had to amputate it for her to have a healthy life. At 14 years old, doctors verbatim said she had the lung of a 30-year-old that worked in the coal mines."<ref>Saitta, [https://www.wtkr.com/news/in-the-community/newport-news/newport-news-residents-say-coal-dust-is-the-source-of-some-health-problems Newport News residents say coal dust is the source of some health problems], ''3WTKR'', April 20, 2024. </ref> | [[Interviews and Oral Histories|Interviews with residents]] of Southeast Newport News and Lambert’s Point reveal that asthma and other respiratory health impacts are widespread and a major issue of community concern. One resident of Southeast Newport News, Uneita Scott, reported that her sister became sick from exposure to coal dust as a child: "Her diagnosis was a coal miner's lung so they had to amputate it for her to have a healthy life. At 14 years old, doctors verbatim said she had the lung of a 30-year-old that worked in the coal mines."<ref>Saitta, [https://www.wtkr.com/news/in-the-community/newport-news/newport-news-residents-say-coal-dust-is-the-source-of-some-health-problems Newport News residents say coal dust is the source of some health problems], ''3WTKR'', April 20, 2024. </ref> | ||
== Documents == | == Documents == | ||
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Integrated Science Assessment (ISA) for Particulate Matter, 2019 | * [[:File:State-of-the-Air-2025.pdf|American Lung Association, State of the Air, 2025]] | ||
* [[:File:ISA PM FINAL2019.PDF|U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Integrated Science Assessment (ISA) for Particulate Matter, 2019]] | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
Latest revision as of 17:35, 4 June 2025
Airborne Particles
Exposure to air pollution––especially particles––is the second leading risk factor for mortality globally (behind only high blood pressure), contributing to approximately 8 million deaths each year.[1] Particles are very harmful,[2][3][4] with chronic exposure to particulates shortening our lives by an average of 1–3 years.[5][6][7] Chronic and acute exposure to particles has also been linked to: increased risk of death from cardiovascular disease;[8][9][10][11][12][13][14][15][16][17][18] diminished lung function and damage to the small airways of the lungs;[19][20][21][22][23] increased hospitalization for asthma attacks for children;[24][25][26][27] slowed lung function growth in children and teenagers;[28][29][30] increased risk of lower birth weights and infant mortality;[31][32][33][34][35][36] elevated risk of developing type-2 diabetes;[37][38][39] cognitive impacts, including links to dementia, Alzheimer’s Disease, and Parkinson’s Disease;[40][41][42][43] and increased risk of mental health issues such as depression.[44] There is no safe level of exposure to particle pollution.[45][46]
The health impacts of particles are influenced by particle size, composition, and shape.
- Size: Particles are regulated based on size, with size also affecting how deeply particulates penetrate into the human body and their health impacts.[47] Large particles like dust (PM10) deposit rapidly after inhalation, mostly settling into our upper respiratory tract. Fine particles (PM2.5) reach the lower respiratory tract and lungs, and very-fine particles (PM1) tend to settle deep in the lungs and alveoli, the tiny air sacs where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged between the lungs and blood during breathing. Ultrafine particles (PM0.1) are small enough to penetrate cell walls to enter the bloodstream. All else being equal, breathing dust is not thought to be as harmful to our health as breathing in smaller particles. However, there is research identifying health impacts of exposure to PM10 specifically, for example, asthma diagnosis prevalence and asthma-related emergency department visits in children.[25]
- Composition: Particles, including dust, be made of a wide variety of materials such as oils, heavy metals, salts, and black carbon, also known as soot, which each causing different health impacts. Particles with high concentrations of toxic metals have been shown to be especially harmful than particles on average.[48][49][50] For example, researchers found a higher risk of hospitalization associated with short-term PM2.5 with higher concentrations of nickel, vanadium, and elemental carbon.[48] For people living near a major source of metals, concentrations over toxic metals in airborne PM10 have been found to correlate with metals concentrations in residents' blood.[51]
- Shape: Particle shape can also be important. In perhaps the most well known example, asbestos particles are long, thin fibers that, because of their shape, can become permanently lodged in the lungs, leading to lung cancer and mesothelioma.[52]
Coal Dust
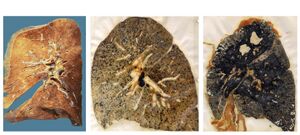
Coal dust is a component of particulate matter. The majority of research on the health impacts of coal dust has come from studies on occupational exposures of coal miners. Miners’ inhalation exposure to coal dust has been shown to place them at an increased risk of developing Coal Workers’ pneumoconiosis (CWP), also known as coal miner’s lung, black lung disease, or progressive massive fibrosis, as well as lung cancer, decreased lung function, and other health impacts.[54][55][56][57][58]
Coal dust typically contains high levels of toxic metals, including mercury (Hg), lead (Pb), arsenic (Ar), cadmium (Cd), as well as crystalline silica. These substances are harmful when inhaled or ingested and are known to cause cancer, fetal defects, and neurological damage, even at very low doses. Coal dust also contains high levels of transition metals, including iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), and copper (Cu) that can induce oxidative stress in our bodies.[54] Because coal dust has high concentrations of metals, there is reason to believe it causes harm at exposures below PM10 National Ambient Air Quality Standards, with there being so safe level of PM2.5 composed of any material.[45][46] Researchers have measured elevated metals with known health impacts in the soils near coals mines and terminals, for example, selenium (Se) in the vicinity of mountaintop coal mines in the Elk Valley, British Columbia, Canada[59] and arsenic near the Norfolk Southern Terminal in Lambert's Point, Norfolk.[60]
There is a body of research identifying an array of adverse health impacts on communities living near coal mines and areas of coal-related activities, particularly in Appalachia[61][62][63][64][65][66][67] but other locations as well.[68][69][70][71][72] These include: higher rates of lung, kidney, and heart disease, even for people who never worked in a mine; worse adjusted health status and with higher rates of cardiopulmonary disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and hypertension;[61][63][66][67] more days of self-rated poor physical and/or mental health and activity limitation;[62][73] higher mortality, including from lung cancer;[64] more frequent birth defects;[65] more prevalent respiratory symptoms and/or more severe respiratory symptoms in elementary school-aged children that were exposed to coal dust;[68][70][71] poorer learning outcomes;[74] and elevated lead and cadmium in the blood of children ages 6 months–6 years[69] and elevated selenium and zinc in the urine of children ages 6–11 years[72] living in coal-mining areas.
Comparable studies have not been done to assess health impacts on residents living near coal export facilities in Hampton Roads. There are references to a 2005 study by the Peninsula Health District purporting to show that Southeast Newport News residents visited the emergency room for asthma at a rate double that of both Newport News and Virginia on average. However, a copy of the document can not be found.
Interviews with residents of Southeast Newport News and Lambert’s Point reveal that asthma and other respiratory health impacts are widespread and a major issue of community concern. One resident of Southeast Newport News, Uneita Scott, reported that her sister became sick from exposure to coal dust as a child: "Her diagnosis was a coal miner's lung so they had to amputate it for her to have a healthy life. At 14 years old, doctors verbatim said she had the lung of a 30-year-old that worked in the coal mines."[75]
Documents
- American Lung Association, State of the Air, 2025
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Integrated Science Assessment (ISA) for Particulate Matter, 2019
References
- ↑ State of Global Air, Health Impacts of Air Pollution.
- ↑ American Lung Association, State of the Air, Health Impact of Air Pollution, 2025.
- ↑ U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Integrated Science Assessment (ISA) for Particulate Matter, 2019.
- ↑ Liu et al., Ambient Particulate Air Pollution and Daily Mortality in 652 Cities, The New England Journal of Medicine, 381, 8, 705–715, 2019.
- ↑ State of Global Air, Impact of Air Pollution on Life Expectancy.
- ↑ Greenstone et al., Air Quality Life Index, Annual Update, 2024.
- ↑ Pope III et al., Fine-Particulate Air Pollution and Life Expectancy in the United States, The New England Journal of Medicine, 360, 4, 376–386, 2009.
- ↑ Dockery et al., An Association between Air Pollution and Mortality in Six U.S. Cities, The New England Journal of Medicine, 329, 24, 1753–1759, 1993.
- ↑ Pope et al., Particulate Air Pollution as a Predictor of Mortality in a Prospective Study of U.S. Adults, American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 151, 3, 1995.
- ↑ Brunekreef et al., Effects of Long-Term Exposure to Traffic-Related Air Pollution on Respiratory and Cardiovascular Mortality in the Netherlands: The NLCS-AIR Study, Health Effect Institute Research Report, 139, 2009.
- ↑ Eftim et al., Fine Particulate Matter and Mortality: A Comparison of the Six Cities and American Cancer Society Cohorts with a Medicare Cohort, Epidemiology, 19, 2, 209–216, 2008.
- ↑ Laden et al., Reduction in Fine Particulate Air Pollution and Mortality: Extended Follow-Up of the Harvard Six Cities Study, American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 173, 6, 667–672, 2006.
- ↑ Miller et al., Long-Term Exposure to Air Pollution and Incidence of Cardiovascular Events in Women, The New England Journal of Medicine, 356, 5, 447–458, 2007.
- ↑ Pope III et al., Cardiovascular Mortality and Long-Term Exposure to Particulate Air Pollution: Epidemiological Evidence of General Pathophysiological Pathways of Disease, Circulation, 109, 1, 71–77, 2004.
- ↑ Puett et al., Chronic Particulate Exposure, Mortality, and Coronary Heart Disease in the Nurses’ Health Study, American Journal of Epidemiology, 168, 10, 1161–1168, 2008.
- ↑ Puett et al., Chronic Fine and Coarse Particulate Exposure, Mortality, and Coronary Heart Disease in the Nurses’ Health Study, Environmental Health Perspectives, 117, 11, 1697–1701, 2009.
- ↑ Samet et al., Fine Particulate Air Pollution and Mortality in 20 U.S. Cities, 1987–1994, The New England Journal of Medicine, 343, 24, 1742–1749, 2000.
- ↑ Zanobetti et al., The Effect of Fine and Coarse Particulate Air Pollution on Mortality: A National Analysis, Environmental Health Perspectives, 117, 6, 898–903, 2009.
- ↑ Wu et al., Case Report: Lung Disease in World Trade Center Responders Exposed to Dust and Smoke: Carbon Nanotubes Found in the Lungs of World Trade Center Patients and Dust Samples, Environmental Health Perspectives, 118, 4, 499–504, 2010.
- ↑ Zhang et al., Long-Term Exposure to Diesel Engine Exhaust Induced Lung Function Decline in a Cross Sectional Study, Industrial Health, 55, 1, 13–26, 2017.
- ↑ Cui et al., Association between Bedroom Particulate Matter Filtration and Changes in Airway Pathophysiology in Children with Asthma, Journal of the American Medical Association Pediatrics, 174, 6, 533–542, 2020.
- ↑ Karr et al., Effects of Subchronic and Chronic Exposure to Ambient Air Pollutants on Infant Bronchiolitis, American Journal of Epidemiology, 165, 5, 553–560, 2007.
- ↑ Leikauf et al., Mechanisms of Ultrafine Particle-Induced Respiratory Health Effects, Experimental & Molecular Medicine, 52, 329–337, 2020.
- ↑ Altman et al., Relationships of Outdoor Air Pollutants to Non-Viral Asthma Exacerbations and Airway Inflammatory Responses in Urban Children and Adolescents: A Population-Based Study, The Lancet Planetary Health, 7, 1, e33–e44, 2023.
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 Keet et al., Long-Term Coarse Particulate Matter Exposure Is Associated with Asthma among Children in Medicaid, American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 197, 6, 737–746, 2017.
- ↑ Tolbert et al., Air Quality and Pediatric Emergency Room Visits for Asthma in Atlanta, Georgia, USA, American Journal of Epidemiology, 151, 798–810, 2000.
- ↑ Schwartz et al., Particulate Air Pollution and Hospital Emergency Room Visits for Asthma in Seattle, American Review of Respiratory Disease, 147, 826–31, 1993.
- ↑ Garcia et al., Air Pollution and Lung Function in Children, Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 148, 1, 1–14, 2021.
- ↑ Raizenne et al., Acute lung Function Responses to Ambient Acid Aerosol Exposures in Children, Environmental Health Perspectives, 79, 179–85, 1989.
- ↑ Thurston et al., Summertime Haze Air Pollution and Children with Asthma, American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 155, 654–660, 1997.
- ↑ Fong et al., Fine Particulate Air Pollution and Birthweight: Differences in Associations along the Birthweight Distribution, Epidemiology, 30, 5, 617–623, 2020.
- ↑ Basu et al., Effects of Fine Particulate Matter and Its Constituents on Low Birth Weight among Full-Term Infants in California, Environmental Research, 128, 42–51, 2014.
- ↑ Dadvand et al., Maternal Exposure to Particulate Air Pollution and Term Birth Weight: A Multi-Country Evaluation of Effect and Heterogeneity, Environmental Health Perspectives, 121, 3, 267–373, 2013.
- ↑ Ebisu et al., Airborne PM2.5 Chemical Components and Low Birth Weight in the Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic Regions of the United States, Environmental Health Perspectives, 120, 12, 1746–1752, 2012.
- ↑ Kloog et al., Using New Satellite Based Exposure Methods to Study the Association between Pregnancy PM2.5 Exposure, Premature Birth and Birth Weight in Massachusetts, Environmental Health, 11, 40, 2012.
- ↑ Stieb et al., Ambient Air Pollution, Birth Weight and Preterm Birth: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Environmental Research, 117, 100–111, 2012.
- ↑ Eze et al., Association between Ambient Air Pollution and Diabetes Mellitus in Europe and North America: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Environmental Health Perspectives, 123, 5, 381-389, 2015.
- ↑ Liu et al., Associations between Long-Term Exposure to Ambient Air Pollution and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Environ Pollution, 252, ptB, 1235–1245, 2019.
- ↑ Wu et al., Ambient Air Pollution Associated with Incidence and Dynamic Progression of Type 2 Diabetes: A Trajectory Analysis of a Population‑Based Cohort, BMC Medicine, 20, 375, 2022.
- ↑ Weuve, et al., Exposure to Air Pollution in Relation to Risk of Dementia and Related Outcomes: An Updated Systematic Review of the Epidemiological Literature, Environmental Health Perspectives, 129, 96001, 2021.
- ↑ Shi et al., Long-Term Effects of PM2.5 on Neurological Disorders in the American Medicare Population: A Longitudinal Cohort Study, Lancet Planetary Health, 4, e557–e565, 2020.
- ↑ Shi et al., Incident Dementia and Long-Term Exposure to Constituents of Fine Particle Air Pollution: A National Cohort Study in the United States, Proceeding of the National Academy of Sciences U.S.A., 120, e2211282119, 2022.
- ↑ Peters, Commentary: Ambient Air Pollution and Alzheimer’s Disease: The Role of the Composition of Fine Particles, Proceeding of the National Academy of Sciences U.S.A., 120, 3, e2220028120, 2023.
- ↑ Gao X et al., Long-Term Air Pollution, Genetic Susceptibility, and the Risk of Depression and Anxiety: A Prospective Study in the UK Biobank Cohort, Environmental Health Perspectives, 131, 1, 2023.
- ↑ 45.0 45.1 Wei et al., Exposure-Response Associations between Chronic Exposure to Fine Particulate Matter and Risks of Hospital Admission for Major Cardiovascular Diseases: Population Based Cohort Study, BMJ, 384, e076939, 2024.
- ↑ 46.0 46.1 Sun et al., Short Term Exposure to Low Level Ambient Fine Particulate Matter and Natural Cause, Cardiovascular, and Respiratory Morbidity among US Adults with Health Insurance: Case Time Series Study, BMJ, 384, e076322, 2024.
- ↑ American Lung Association, Particle Pollution, 2025.
- ↑ 48.0 48.1 Bell et al., Hospital Admissions and Chemical Composition of Fine Particle Air Pollution, American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 179, 12, 1115–1120, 2009.
- ↑ Ostro et al., The Impact of Components of Fine Particulate Matter on Cardiovascular Mortality in Susceptible Subpopulations, Occupational & Environmental Medicine, 65, 750–756, 2008.
- ↑ Ostro et al., The Effects of Components of Fine Particulate Air Pollution on Mortality in California: Results from CALFINE, Environmental Health Perspectives, 115, 13–19, 2007.
- ↑ Gangwar et al., Assessment of Air Pollution Caused by Illegal E-Waste Burning to Evaluate the Human Health Risk, Environment International, 125, 191–199, 2019.
- ↑ American Lung Association, Asbestos, 2025
- ↑ Popovich, Black Lung Disease Comes Storming Back in Coal Country, New York Times, February 22, 2018.
- ↑ 54.0 54.1 Liu et al., The Impacts of Coal Dust on Miners’ Health: A Review, Environmental Research, 190, 109849, 2020.
- ↑ Attfield et al., Occupational and Environmental Respiratory Disease, St. Louis, MO, Mosby, 362–372, 1996.
- ↑ American Lung Association, Learn About Coal Worker’s Pneumoconiosis, 2024.
- ↑ Blackley et al., Progressive Massive Fibrosis in Coal Miners From 3 Clinics in Virginia, Journal of the American Medical Association, 319, 5, 500-501, 2018.
- ↑ United States Government Accountability Office, MINE SAFETY: Reports and Key Studies Support the Scientific Conclusions Underlying the Proposed Exposure Limit for Respirable Coal Mine Dust, August 17, 2012.
- ↑ Petryshen et al., Spatial Distribution of Selenium and other Potentially Toxic Elements Surrounding Mountaintop Coal Mines in the Elk Valley, British Columbia, Canada, Heliyon, 9, 7, e17242, 2023.
- ↑ Bounds et al., Arsenic Addition to Soils from Airborne Coal Dust Originating at a Major Coal Shipping Terminal, Water, Air, and Soil Pollution 185, 195–207, 2007.
- ↑ 61.0 61.1 Hendryx et al., Relations between Health Indicators and Residential Proximity to Coal Mining in West Virginia, American Journal of Public Health, 98, 4, 669–671, 2008.
- ↑ 62.0 62.1 Zulling et al., Health-Related Quality of Life Among Central Appalachian Residents in Mountaintop Mining Counties, American Journal of Public Health, 101, 5, 848–853, 2011.
- ↑ 63.0 63.1 Hendryx, Mortality from Heart, Respiratory, and Kidney Disease in Coal Mining Areas of Appalachia, International Archives of Occupational and Environmental Health, 82, 243–249, 2008.
- ↑ 64.0 64.1 Hendryx et al., Lung Cancer Mortality is Elevated in Coal-Mining Areas of Appalachia, Lung Cancer, 62, 1, 1–7, 2007.
- ↑ 65.0 65.1 Ahern et al., The Association between Mountaintop Mining and Birth Defects among Live Births in Central Appalachia, 1996–2003. Environmental Research, 111, 6, 838–846, 2011.
- ↑ 66.0 66.1 Hendryx et al., Higher Coronary Heart Disease and Heart Attack Morbidity in Appalachian Coal Mining Regions, Preventive Medicine, 49, 5, 355–359, 2009.
- ↑ 67.0 67.1 Hendryx et al., Hospitalization Patterns Associated with Appalachian Coal Mining, Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health, 24, 2064–2070, 2007.
- ↑ 68.0 68.1 Brabin et al., Respiratory Morbidity in Merseyside Schoolchildren Exposed to Coal Dust and Air Pollution, Archives of Disease in Childhood, 70, 4, 305–312, 1994.
- ↑ 69.0 69.1 Yapici et al., Lead and Cadmium Exposure in Children Living around a Coal-Mining Area in Yatağan, Turkey, Toxicology and Industrial Health, 22, 357–362, 2006.
- ↑ 70.0 70.1 Howel et al., Consultations of Children Living near Open-Cast Coal Mines, Environmental Health Perspectives, 109, 567–71, 2001.
- ↑ 71.0 71.1 Pless-Mulloli et al., Living near Opencast Coal Mining Sites and Children's Respiratory Health, Occupational & Environmental Medicine, 57,145–51, 2000.
- ↑ 72.0 72.1 Santos et al., Biomonitoring of Trace Elements in Urine Samples of Children from a Coal-Mining Region, Chemosphere, 197, 622–626, 2018.
- ↑ Zullig et al., A Comparative Analysis of Health-Related Quality of Life for Residents of U.S. Counties with and without Coal Mining, Public Health Reports, 125, 548–555, 2010.
- ↑ Cain et al., Learning Outcomes among Students in Relation to West Virginia Coal Mining: an Environmental Riskscape Approach, Environmental Justice, 3, 2, 71–77, 2010.
- ↑ Saitta, Newport News residents say coal dust is the source of some health problems, 3WTKR, April 20, 2024.